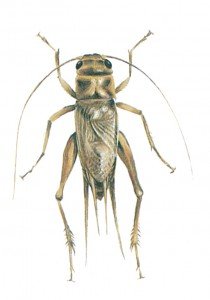
(The House Cricket)
Latin: Acheta domestica.
The house cricket is closely related to the grasshopper. Both have developed the rear pair of legs to be jumping legs. Originally it came from North Africa. In the past, bakeries were the typical residence of house crickets. Today it has become a common insect in homes, where it mainly lives in boiler rooms. In food businesses, you can find it in boiler rooms, heating ducts, and warm, moist production facilities. House crickets eat almost any kind of organic material, and have a certain fondness for soft things (vegetables, fruit, flour products and meat). The sharp, biting mouth parts can also bite holes in textiles and plastics, which the insect do not eat. As possible disease carriers and polluters, they must be treated as seriously as cockroaches.

In this country they cannot survive outdoors in winter, except in waste dumps, etc., where fermenting waste creates heat and provides a food source. From the waste dumps crickets invade nearby buildings massively. The female house cricket can lay approximately 1000 eggs within 5 weeks. They are usually placed in a hole as the female bores in moist soil with its egg laying spike (the ovipositor). When lacking moist soil, the eggs can also be placed in damp paper or moist foods. Crickets are among the insects that have incomplete metamorphosis. This means that, like cockroaches, booklice and earwigs, it gives birth to offspring that looks like the adult, but is somewhat smaller. The offspring become sexually mature at 22 ° C in 10 months. At 30 ° C it takes only a few months and below 20 ° C its development is so slow that babies die before they become adults.
House crickets can be exterminated by treating cracks and fissures near heaters, where they are hiding, with an insect powder or a spray. In the case of individual insects, a little bread soaked in a mixture of white beer, sugar and 10% borax will often do the trick.




